Healthwise
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.
Helicobacter Pylori (H. Pylori) Tests
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)tests are used to detect a Helicobacter pylori bacterial infection in the stomach and upper part of the small intestine (duodenum). H. pylori can cause peptic ulcers. But most people with H. pylori in their digestive systems do not develop ulcers.
Several tests are used to detect H. pylori:
- Urea breath test. A urea breath test checks to see if you have H. pylori bacteria in your stomach. This test can show if you have an H. pylori infection. It can also be used to see if treatment has worked to get rid of H. pylori.
- Stool antigen test. A stool antigen test checks to see if substances (called antigens) that trigger the immune system to fight an H. pylori infection are present in your feces (stool). Stool antigen testing may be done to confirm a diagnosis of H. pylori infection or to find out if treatment for an H. pylori infection has worked.
- Stomach biopsy. A small tissue sample (biopsy) is taken from the lining of your stomach and small intestine during an endoscopy. Several different tests may be done on the biopsy sample.
- Blood antibody test. Occasionally, a blood test is done to check to see whether your body has made antibodies to H. pylori bacteria. If you have antibodies to H. pylori in your blood, it means you either are currently infected or have been infected in the past. This test is not as accurate as the other tests.
Why It Is Done
H. pylori tests are done to:
- Find out if an infection with H. pylori bacteria may be causing an ulcer or irritation of the stomach lining (gastritis).
- Find out if treatment for the infection worked.
How To Prepare
Blood antibody test
You do not need to do anything before you have this test.
Urea breath test, stool antigen test, or stomach biopsy
Medicines may change the results of these tests. Be sure to tell your doctor about ALL the medicines, vitamins, supplements, and herbal remedies you take. Your doctor may advise you to stop taking some of them.
- Do not take antibiotics or medicines containing bismuth (such as Pepto-Bismol) for 1 month before the test.
- Do not take proton pump inhibitors for 2 weeks before the test.
Urea breath test or stomach biopsy
You will be asked to not eat or drink anything for a certain amount of time before your breath test or stomach biopsy. Follow your doctor's instructions about how long you need to avoid eating and drinking before the test. If you are going to have a stomach biopsy, your doctor will give you instructions on how to prepare.
Many medicines may change the results of these tests.
- Do not take antibiotics or medicines containing bismuth (such as Pepto-Bismol) for 1 month before the test.
- Do not take proton pump inhibitors or H2 blockers for 2 weeks before the test.
How It Is Done
Blood antibody test
A health professional uses a needle to take a blood sample, usually from the arm.
Urea breath test
A breath sample is collected when you blow into a balloon or blow bubbles into a bottle of liquid. The health professional will:
- Collect a sample of your breath before the test starts.
- Give you a pill, a liquid, or some water to swallow that contains a special substance called urea.
- Collect more samples of your breath. The samples will be tested to see if they contain carbon dioxide, which is formed when H. pylori comes into contact with the urea.
Stool antigen test
For this test, you may be asked to collect the stool sample at home. To collect the sample, you need to:
- Put on gloves before handling your stool. Stool can contain germs that spread infection.
- Urinate before you collect the stool. Then pass stool into a dry container. Either solid or liquid stools can be collected. Be careful not to get urine or toilet tissue in with the stool sample.
- Replace the container cap. Label the container with your name, your doctor's name, and the date the sample was collected.
- Wash your hands well after you collect the sample and take off your gloves.
- Take the sealed container to your doctor's office or to the lab as soon as you can.
Sometimes a stool sample is collected during the exam using a rectal swab. The swab is inserted into the rectum, rotated gently, and then pulled out. It is placed in a clean, dry container and sent to the lab right away.
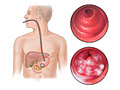
Stomach biopsy
A procedure called endoscopy is used to collect samples of tissue from the stomach and the first part of the small intestine. The tissue samples are tested in a lab to see if they contain H. pylori.
How It Feels
Blood antibody test
When a blood sample is taken, you may feel nothing at all from the needle. Or you might feel a quick sting or pinch.
Urea breath test
This test usually doesn't cause any pain or discomfort.
Stool antigen test
This test usually doesn't cause any pain or discomfort if you collect a stool sample at home.
If your doctor collects the sample during a rectal exam, you may feel some pressure or discomfort as the cotton swab is inserted into your rectum.
Stomach biopsy
A procedure called endoscopy is used to collect samples of tissue from the stomach and the first part of the small intestine.
The doctor may spray medicine on the back of your throat to numb it. It usually tastes slightly bitter.
You also will get medicine to prevent pain and to relax you through an intravenous (I.V.) needle that is placed in a vein in your arm. You may notice a brief, sharp pain when the I.V. is placed in your arm.
The doctor will guide an endoscope through your mouth toward the back of your throat. The doctor will tell you when to swallow. This helps the scope move down your throat. You will be able to breathe normally. The doctor will move the scope down your esophagus into your stomach to take the biopsy. You will not feel anything when the biopsy is taken.
Risks
Blood antibody test
There is very little chance of having a problem from this test. When a blood sample is taken, a small bruise may form at the site.
Urea breath test
There are no known risks or complications with a urea breath test. The urea test uses a small amount of radioactive carbon, but the amount of exposure is extremely small—less than you normally get from being outside during the day.
Stool antigen test
There are no risks or complications with a stool sample.
Biopsy
There is a slight risk of puncturing the wall of the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum during an endoscopy to collect biopsy samples. The biopsy may also cause some mild bleeding in the digestive system where the samples are collected. But the bleeding usually stops without treatment.
Results
Results from the urea breath test or a stool antigen test are usually available within a few hours. Results from a blood antibody test are usually available within 24 hours. Results from biopsy samples obtained by endoscopy are usually available within 48 hours. Results from a biopsy sample that is cultured can take up to 10 days.
Blood antibody test
Normal: The blood sample does not contain H. pylori antibodies.
Abnormal: The blood sample contains H. pylori antibodies.
Urea breath test
Normal: The breath sample does not contain the carbon dioxide that would form if an H. pylori infection were present.
Abnormal: The breath sample contains the tagged carbon dioxide.
Stool antigen test
Normal: The stool sample does not contain H. pylori antigens.
Abnormal: The stool sample contains H. pylori antigens.
Biopsy
Normal: The biopsy sample does not contain H. pylori bacteria.
Abnormal: The biopsy sample contains H. pylori bacteria.
Related Information
Credits
Current as of: September 30, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: September 30, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2026 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.